Placing breast implants under the muscle is a popular option which can be done in one of two possible methods. The implant can be partially or totally positioned under the pectoralis muscles of the chest. Submuscular placement remains the most popular style of breast augmentation and has distinct advantages and disadvantages when compared to subglandular implant positioning.
This article details the invasive procedures which are used to position breast prostheses fully or partially under the chest muscles.
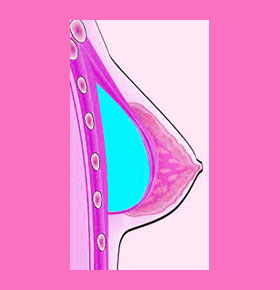
Breast Implants Under the Muscle / Total Submuscular
Total submuscular placement is achieved by implanting the prosthesis completely under the pectoralis muscle. This approach is a more invasive surgery than subglandular placement and women will have to endure a longer and more painful recovery period.
Complications are more common with this placement, including bleeding, implant displacement and continuing pain. Submuscular implants often distort during vigorous athletic activities creating a strange appearance. Some active women find this placement to cause an uncomfortable sensation, which can interfere with their physical abilities.
Saline implants have a greater chance of rupturing when placed under the muscle.
One definitive benefit of submuscular placement includes total coverage for the implant shell. This creates a less visible and palpable implant, especially in women with naturally smaller breasts.
Mammography is not affected using submuscular implantation, since the pectoralis muscle acts as a barrier between the breast tissue and the implant.
Capsular contracture is also less common when placing breast prostheses under the chest muscles, due to the movement of the muscular tissue against the implant shell.
Partial Submuscular Breast Implants
Placing the implant partially under the muscle is a very popular option in modern breast enlargement. This approach is commonly called subpectoral or dual plane placement.
In this procedure, the implant is positioned so that the top portion of the implant is covered by the pectoralis major muscle and the lower portion is free in the subglandular plane. This procedure is a great compromise between full submuscular and subglandular, in that the top of the implant is well covered, but the breast still feels and contours like a natural bosom.
This placement creates very natural looking cleavage and allows the breast to round out as expected at the bottom. Incidence of capsular contracture is greatly reduced using this approach.
The operation is invasive and requires a longer and more uncomfortable recovery than subglandular implantation. Some women report strange sensations when using their chest muscles during athletics, due to this implant placement.
Breast Implants Under the Muscle Compromises
Submuscular placement is an important development in cosmetic breast surgery. Total submuscular placement is particularly good for women with very small natural breasts or women who require more supportive tissue to hold the implant due to breast reconstruction surgery.
Partial submuscular is advised for most women due to its excellent aesthetics, natural feel and reduced chance for experiencing symptomatic contracture.
Talk to your surgeon about which placement is best for your particular body type and lifestyle.
Implants can usually be moved from one placement location to another during subsequent surgeries. However, it is better to learn the facts of each placement and try to make the best choice the first time around.



