Endoscopic breast enlargement is breast augmentation surgery which is performed using an endoscope to visualize the interior of the breast. This advanced tool eliminates the need to create any surgical incision on the breast itself.
Endoscopic augmentation can be performed through the belly button or through the underarm. The main advantages of these types of minimally invasive procedures are to reduce scar formation and keep scars off the breasts.
This essay explores endoscopic cosmetic surgery of the breast and how it has revolutionized the aesthetic industry.
Definition of Endoscopic Breast Enlargement
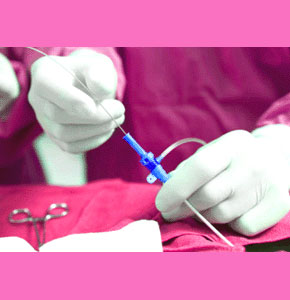
The endoscope is a technologically advanced piece of medical equipment, which is used for numerous applications in a variety of surgical fields. The endoscope is basically one or more quality optical sensors combined with a light source (typically fiber optic).
This live-action camera is mounted in a flexible tube, which is inserted into the body to see where the breast implants are to be positioned. Utilizing this camera and manual manipulation of the anatomical tissue, the surgeon can place the implants in precisely the correct location without ever having to cut into the actual breast tissue.
Transumbilical Breast Enlargement
TUBA is another name for transumbilical breast augmentation and is performed through a small incision placed in the upper part of the navel.
The surgeon will use a blunt dissector to create a tunnel through the abdominal tissue and into the breast. The doctor will use the endoscope to visualize the tunnel and breast interior, and then place a rolled up, unfilled saline breast implant into the newly created pocket.
This method of augmentation leaves no visible scar on the body and allows implant placement above the muscle, under the muscle or even in the dual plane position.
Once the implants are in place, the surgeon will fill the prosthesis shells with sterile saline filler solution and close the small surgical wound, completing the operation.
Transaxillary Endoscopic Breast Enlargement
Transaxillary breast augmentation utilizes a small surgical incision placed in a natural fold of the armpit.
The surgeon will create a tunnel through the axilla to the breast interior using their fingers and possibly a blunt dissector. The surgeon will use the endoscope to see into the new breast pocket and then place the implant in the correct position.
This approach is sometimes performed without an endoscope, using feel alone, but this can cause certain surgical complications in some patients. The endoscope allows better control for preventing injury to healthy tissue, nerve damage and over-dissection of the implant pocket.
This procedure can be used with saline or silicone breast implants. The surgeon can place the implant in any of the submuscular, subpectoral or subglandular positions.
Once in place, the saline implant is filled (a step which is not required when using silicone) and the small incision is closed.
Advantages of Endoscopic Breast Augmentation
The endoscope allows easy access to the breast interior, without damaging the sensitive skin on the surface. This is crucial to allow scarless augmentation in patients who will do anything to avoid telltale marks on the actual breast or areola.
Although some surgeons perform these procedures without the use of the endoscope, it is advisable to insist on its use, in order to make sure everything goes well inside.
Endoscopic surgery is responsible for allowing a wide range of minimally invasive techniques in modern medicine. To learn more about how the endoscope can assist your doctor in performing a perfect breast enlargement procedure, contact a qualified cosmetic surgeon near you.




